Mesoscopic law of stress and fracture evolution of coal seams hydraulic fracturing
-
摘要: 水力压裂作为煤层强化增透技术的一种,其应力演化特征及裂隙形态与扩展范围的判断尤为重要。采用离散元数值方法,以导向压裂为背景,建立水力压裂流固耦合模型;通过应力路径、裂纹热点图等手段,探究水力压裂过程中压裂排量、泊松比、天然裂隙密度对应力演化和裂隙演化的影响及其细观规律。结果表明:不同压裂排量下的应力演化方向及最终应力路径曲线形状有着明显的不同,低排量下裂隙附近的应力比值逐渐增大,而在高排量下先增大后减小;煤层泊松比越大,平均压裂半径越低,但对起裂时间及裂隙的扩展形态影响不明显;天然裂隙的发育情况对水力裂隙的扩展起着关键性作用,高裂隙发育煤层水力裂隙扩展的方向性无法预测,应力演化方向会出现反转现象;压裂过程中不同区域的应力演化特征能够反映出裂隙的扩展状态,现场可通过监测压裂区域附近应力变化,判断水力压裂缝网的扩展范围。Abstract: Hydraulic fracturing is a technology to increase coal seam permeability, and its stress evolution characteristics and the judgment of fracture morphology and propagation range are particularly important. In this paper, based on directional fracturing, a fluid-structure coupling model of hydraulic fracturing is established by using the discrete element numerical method. The effects of fracturing flow, Poisson’s ratio, natural fracture density on stress evolution and fracture evolution, and their mesoscopic laws are investigated by means of the stress path and crack hot spot diagram. The results show that the stress evolution direction and the final stress path curve shape are obviously different at different fracturing rates. The stress ratio near the crack increases gradually at a low fracturing rate, but increases first and then decreases at a high fracturing rate. The larger the Poisson’s ratio, the smaller the fracture radius, but its influence on fracture initiation time and fracture propagation morphology is not obvious. The development of natural fractures plays a key role in the propagation of hydraulic fractures, and the direction of fracture propagation is more random in coal seams with high natural fracture development, and the direction of stress evolution is reversed. The stress evolution characteristics of different regions can reflect the propagation state of fractures in the fracturing process, the propagation range of the hydraulic fracture network can be determined by monitoring the triaxial stress of several fixed positions near the fracture zone.
-
Keywords:
- hydraulic fracturing /
- stress evolution /
- crack evolution /
- mesoscopic law /
- discrete element
-
煤炭资源开采过程中,水力压裂技术作为煤层强化增透的一种技术手段,在一定程度上能提高煤层的透气性,降低瓦斯抽采达标时间,提高抽采浓度,弱化煤层顶底板强度[1-3]。在压裂工程实践中,利用缝槽或导向孔控制裂隙扩展方向,形成压裂缝网,可实现压裂区域的整体增透[4]。然而,裂隙的扩展方向除了受原始地应力及缝槽的影响,也会因煤层物性参数、压裂工艺方法的差异表现出不同的压裂效果,对后续煤层开采产生影响。因此,开展水力压裂应力演化特征及裂隙形态的研究尤为重要,对提高水力压裂技术的科学性,评估压裂效果有重要意义[5]。
前人在理论方面开展压裂增透效果的影响因素研究。程玉刚[6]探究了水力割缝对水力压裂裂隙导向起裂扩展的导向机理,白雪元等[7]建立了拉格朗日元与离散元耦合的连续−非连续数值解法,其计算出的定向射孔水力压裂结果对比GKD模型理论解有较高的正确性,董卓等[8]依托ANAYS软件,探究了材料泊松比、注水压力对裂纹偏转角及裂纹扩展路径的影响,得出上述参数的拟合公式及相关系数。Wang Tao[9]、刘顺[10]等通过对水力裂缝与天然裂缝在不同倾角、间距、应力条件下的交错延伸规律进行量化模拟,优化了水力裂缝与非连续天然裂缝网络的交互模型。在物理实验研究方面,Ge Zhaolong[11]、ChengYugang[12]等通过实验室真三轴实验,研究人工预置缝槽对水力裂缝扩展的作用,为煤矿井下体积压裂提供了新的技术手段。吴拥政等[13]对煤矿井下砂岩进行大尺寸原位取样,得出原生层理方向与水平应力差影响起裂压力及压裂曲线,这为煤矿顶板压裂参数设计提供参考。贾奇锋等[14]以不同煤体结构煤为研究对象,重点研究了水力裂缝与天然裂隙交互问题,得出不同煤体结构煤的水力裂缝延伸规律,为裂隙发育下的抽采孔布置提供了依据。
前人的研究着重于水力压裂中不同因素对裂缝最终扩展形态的影响,对压裂过程中裂隙与应力演化规律的分析较少。笔者采用离散元数值方法,以导向压裂为背景,采用应力路径、裂缝热点图等分析手段,对压裂过程进行细观分析,考察不同压裂排量、泊松比、天然裂隙密度等条件下水力压裂裂隙扩展过程中应力与裂隙的细观演化规律,以期为水力压裂范围监测提供支撑。
1 数值模型的构建
1.1 细观参数的确定
基于离散元的颗粒流程序(Particle Flow Code,PFC)对煤体破裂等非连续介质力学问题能更加直观地体现[15]。模型中介质通过刚性颗粒模拟,颗粒之间使用平行黏结模型进行固定,该模型能传递力和力矩,适合模拟煤岩类材料[16]。
煤层的宏观力学参数选自文献[17]中使用的煤层数据,该煤层平均厚度6.23 m,密度1.28 g/cm3,单轴抗压强度32.22 MPa,抗拉强度2.83 MPa,弹性模量均值1.81 GPa。由于细观参数与宏观参数没有良好的对应性,本文采用试错法[18]对单轴压缩及巴西劈裂数值模拟实验进行参数标定。
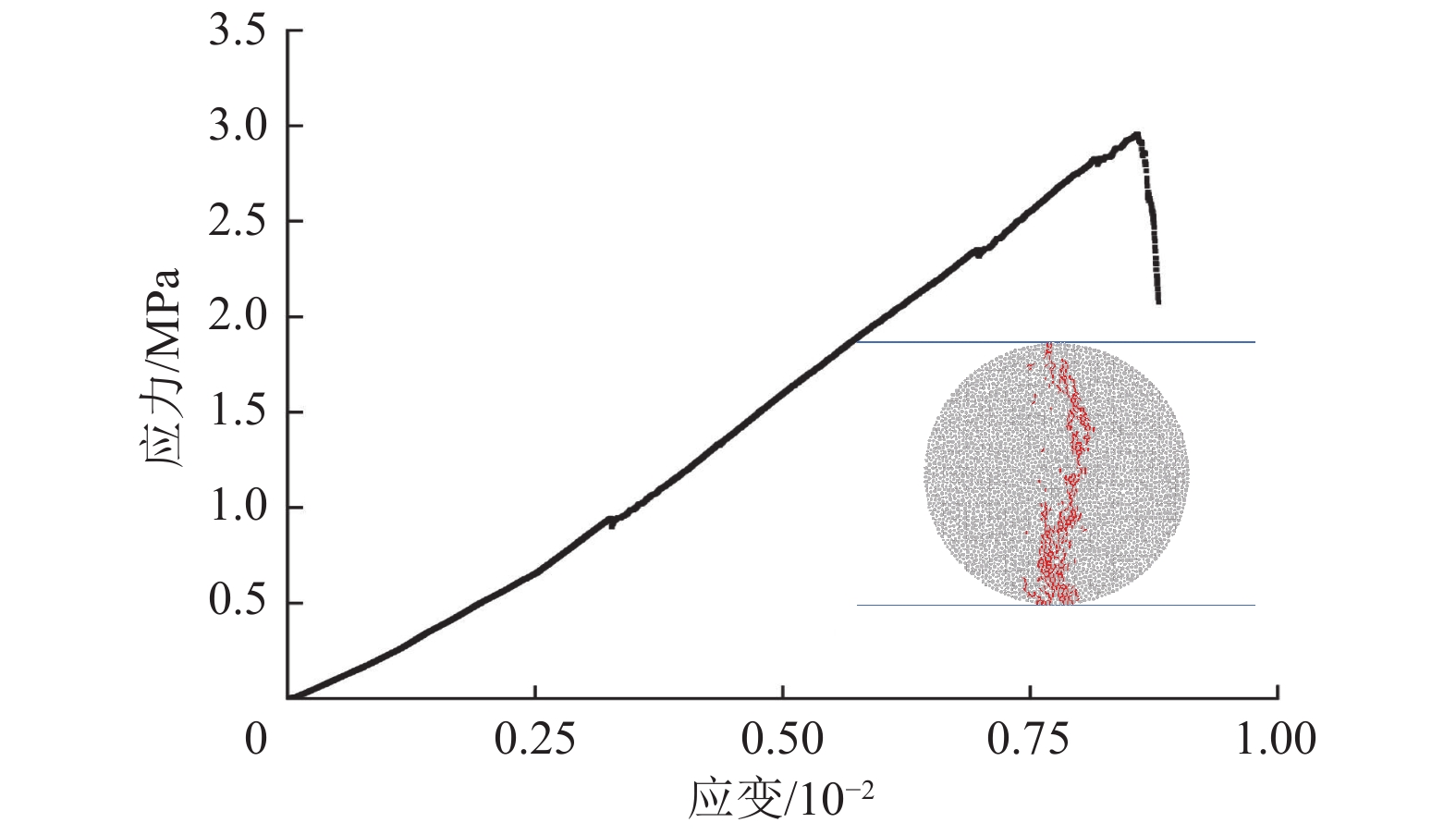
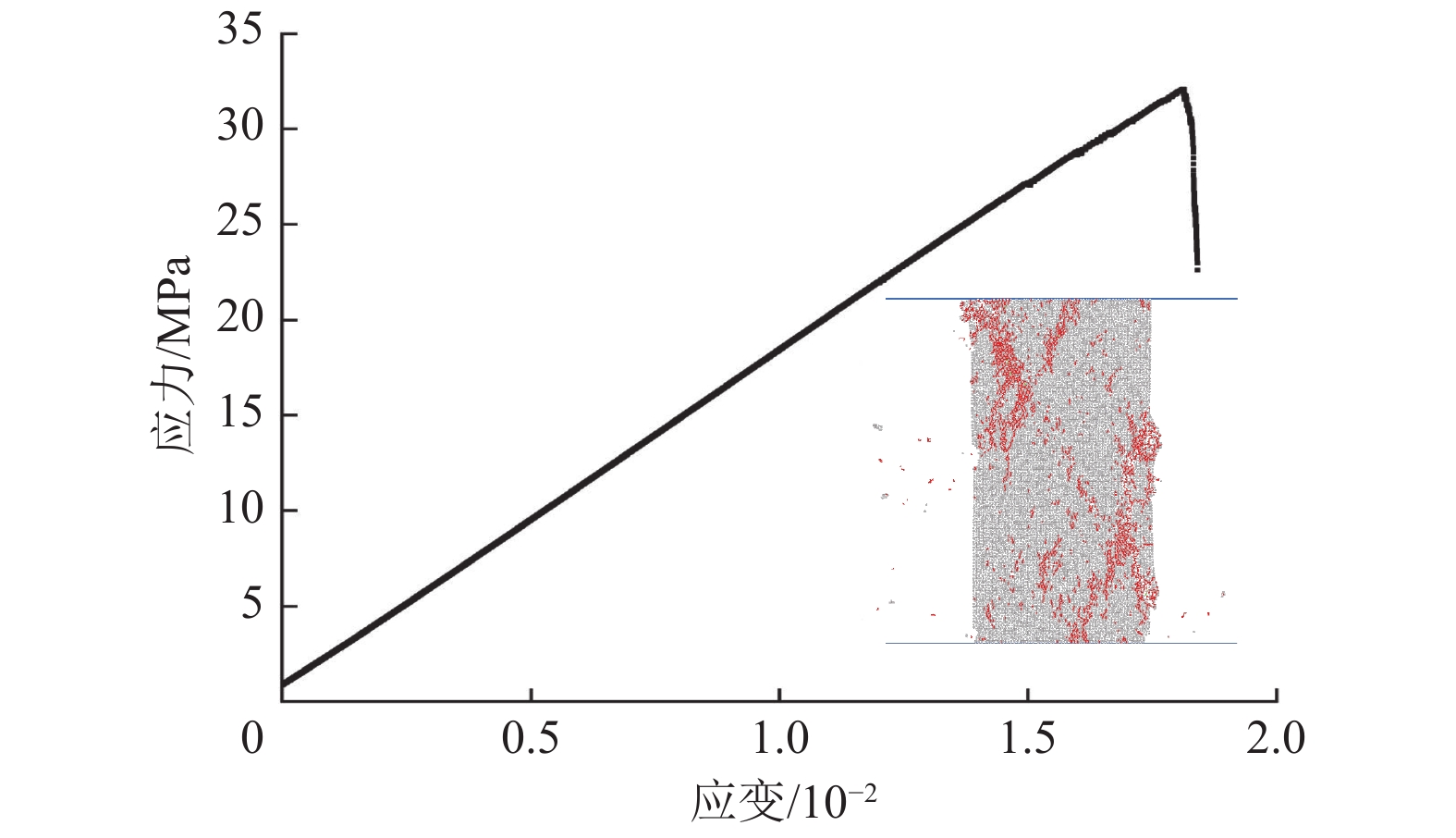
单轴压缩模拟试样尺寸为50 mm×100 mm,颗粒数量为8 838;巴西劈裂模拟试样直径为50 mm,颗粒数量为3 419。标定结果如图1、图2所示,宏观参数见表1,细观参数具体数值见表2,图中红色线段表示加载过程中试样产生的裂隙。
表 1 试样宏观参数与模型宏观参数的比较Table 1. Comparison between sample macro parameters and model macro parameters宏观力学参数 实际值 PFC2D
计算值误差/% 单轴抗压强度σc/MPa 32.22 32.04 −0.5 弹性模量E/GPa 1.81 1.82 0.5 泊松比ν 0.25 本体抗拉强度σt/MPa 2.83 2.96 4.6 表 2 模型细观参数Table 2. Model mesoscopic parameters参数类别 细观参数 数值 颗粒 颗粒最小半径Rmin/mm 0.30 最大最小粒径比Rmax/Rmin 1.66 颗粒密度ρ/(kg∙m−3) 1 280 孔隙率/% 9 阻尼β/(Ns∙m−1) 0.50 接触模型 细观弹性模量Ec/GPa 1.00 刚度比kn/ks 2.30 摩擦因数μ 0.50 细观抗拉强度σc/MPa 11 黏聚力c/MPa 20 摩擦角φ/(°) 37.50 法向临界阻尼比βn 0.57 D. O. Potyondy等[19]指出,平行黏结模型表现出的强度仅与单轴压缩实验相匹配,在模拟巴西劈裂实验时,拉伸强度会过高,与实际值相差较大,但本文标定过程将抗拉强度误差控制在5%以内,标定结果基本符合要求。
1.2 流固耦合的实现方式
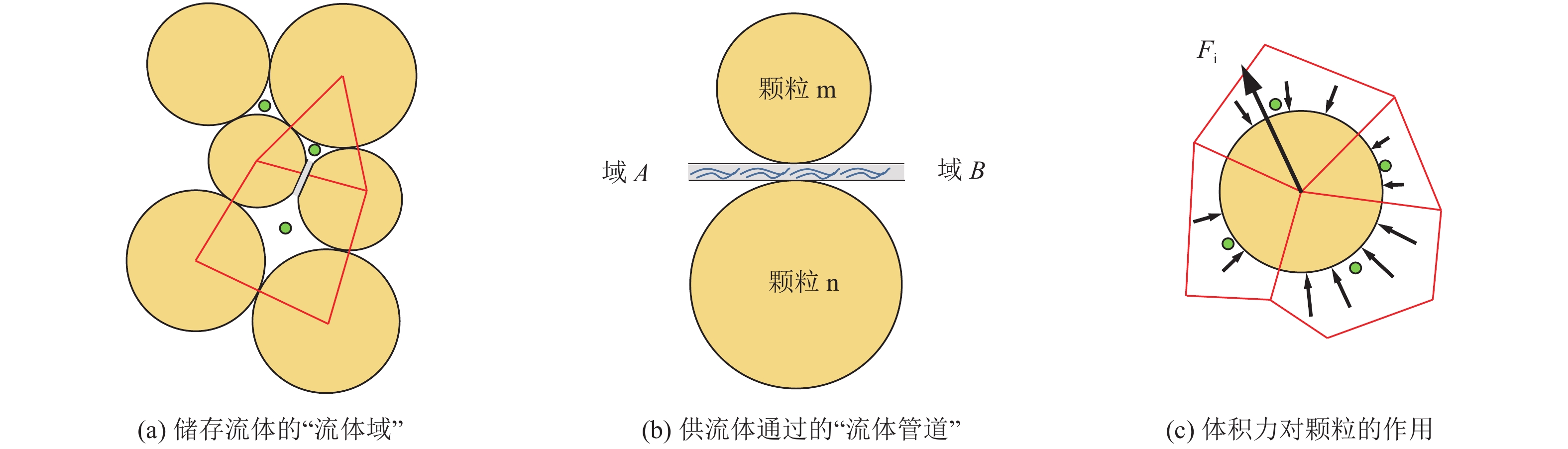
在模型中煤体通过圆形颗粒进行表征,为了表达流体与基质之间的耦合关系,引入管域模型[20]。将模型中颗粒之间构成的空间视为“域”,用于存储流体,如图3a中红色线段围成的多边形;颗粒和颗粒之间存在一个供“域”之间进行流体交换的“管道”,如图3b所示。该“管道”的流量q由微观渗透性系数k、开度a、2个“域”之间的压差∆p和管道长度L共同决定,遵循Hagen-Poiseuille方程:
$$ q = k{a^3}\frac{{\Delta p}}{L} $$ (1) 由上式可以看出,开度a会影响通过流体管道的流量大小,即模型的渗透性。而开度a的大小由颗粒之间的接触状态决定,假设存在一个初始开度a0,当颗粒之间为拉应力时:
$$ a = {a_0} + \lambda \left( {d - {R_1} - {R_2}} \right) $$ (2) 当颗粒之间为压应力时:
$$ a = \frac{{{a_0}{F_0}}}{{F + {F_0}}} $$ (3) 式中:λ为缩放因子;d为两颗粒之间的距离,m;R1、R2为颗粒半径,m;F0为管道开度降为初始开度一半时的法向力,N;F为颗粒当前接触力,N。
模拟的水力压裂过程是以时间步进行的,在一个∆t时间步内,由于流域之间流体交换导致的流域压力变化主要受流体体积压缩模量的影响。假设某个流域有N条流体管道与之连接,则在一个时间步内,流域内的压力变化[21]为:
$$ \Delta p = \frac{{{K_{\text{f}}}}}{{{V_{\text{d}}}}}\left( {\sum {q\Delta t - \Delta {V_{\text{d}}}} } \right) $$ (4) 式中:Kf为流体的体积模量,Pa;Vd为流域体积,m3;∆Vd为流域体积的变化量,m3。
流域内的水压也会对周围的颗粒产生体积力,并作用在颗粒表面,如图3c所示。则颗粒受到的合力为:
$$ {F_{\rm{i}}} = p{{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\rm{i}}}D $$ (5) 式中:p为域内压强,Pa;ni为域中心指向球心的单位矢量;D为颗粒直径,m。
模型整个耦合过程主要体现为以下3点:颗粒之间接触状态的变化影响着流体通道的过水能力,从而影响局部材料渗透率;流体在流域之间的交换引起流域之间的压力变化;流域压力会对周围颗粒产生推移作用。
在整个过程中,交替使用前文的流动方程和压力方程来实现水力压裂现象。为了使模型稳定运行,需要保证域内的压力变化小于扰动压力,当两者相等时可以求出临界时间步长[22]:
$$ \Delta t = \alpha \frac{{2r{V_{\text{d}}}}}{{N{K_{\text{f}}}k{a^3}}} $$ (6) 式中:N为流域所连接的管道数;r为流域周围颗粒的平均半径,m;α为小于1的安全系数。
为了保证在压裂过程中水压能有效地传递,规定产生的裂缝若由水压导致,则该裂缝对应的2个流域内的液体压强等于2个域压力值中的较大值,在保证模型稳定的同时提高了计算效率[23]。
2 模拟方案设计
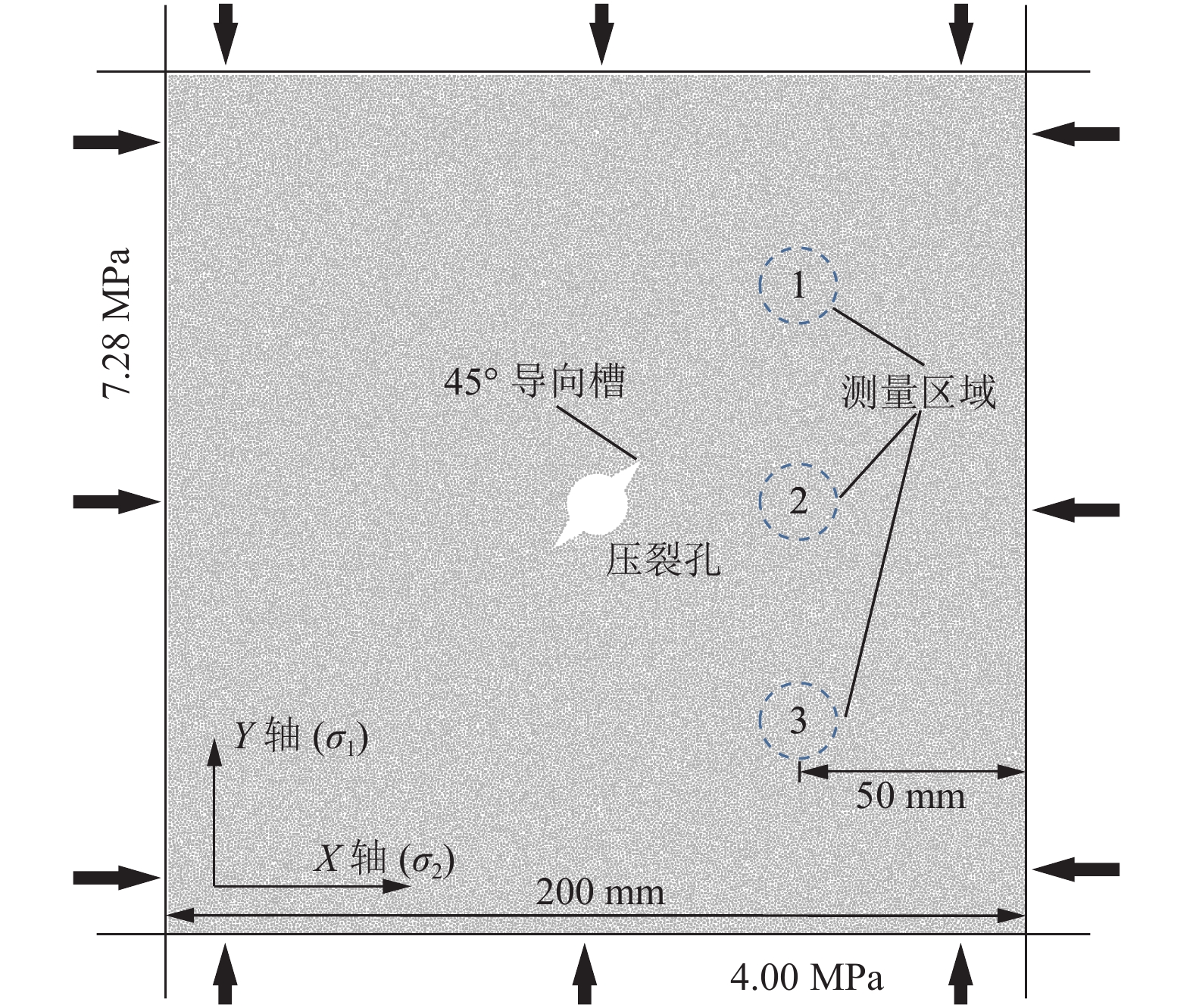
本文采用PFC2D软件建立了200 mm×200 mm的二维离散元模型,模型正中心设置半径为7 mm的压裂孔,并在与X轴方向夹角45°的位置预置了长度为3.5 mm的导向槽模拟导向压裂过程[24-25]。依据文献[26],该煤样所在矿区煤层平均埋深760 m,最大水平主应力为最小水平主应力的1.82倍,故在模型X轴施加7.28 MPa载荷,Y轴施加4.00 MPa载荷模拟煤样所处的实际地应力。为了描述压裂孔附近的应力演化状态,应力监测区域共设置3个,使用测量圆进行监测,距离右侧边界50 mm,均匀垂向布置,用于绘制整个压裂过程中不同区域的应力路径曲线,如图4所示。
模型的四周为透水边界,所有颗粒的运动遵循牛顿第二定律与力−位移定律。模型中采用光滑节理模型来模拟天然裂隙处的力学性质,天然裂隙的长度及角度分布服从幂律分布,统计通过固定参考线的裂隙数量控制天然裂隙的密度。
在现有的研究中,压裂排量、泊松比、天然裂隙密度等因素作为水力压裂研究的热点,它们的改变之所以导致压裂结果不尽相同,是因为这些因素的存在改变了压裂孔周围的应力分布状态,使局部应力发生了重新分布。因此,模拟方案包括以上3个因素,每个因素3个水平,除去1组重复实验,共8组,模拟压裂时间均为140 s。具体模拟实验方案见表3。
表 3 水力压裂模拟方案设计Table 3. Scheme design of hydraulic fracturing simulation序号 天然裂隙
密度煤体泊松比 压裂排量Q/(mL∙min−1) 1 无 0.25 20 2 无 0.25 40 3 无 0.25 60 4 无 0.16 40 5 无 0.35 40 6 低 0.25 40 7 中 0.25 40 8 高 0.25 40 注:低、中、高泊松比分别代表ν = 0.16、ν = 0.25、ν = 0.35;低、中、高压裂排量分别代表Q = 20、Q = 40、Q = 60 mL/min;低、中、高天然裂隙密度分别代表与参考线相交的裂隙数量为5、10、20个。 3 结果分析及讨论
通过绘制压裂过程中的裂纹热点图及监测区域的应力路径,分析不同影响因素下水力压裂区域应力与裂隙细观演化规律。
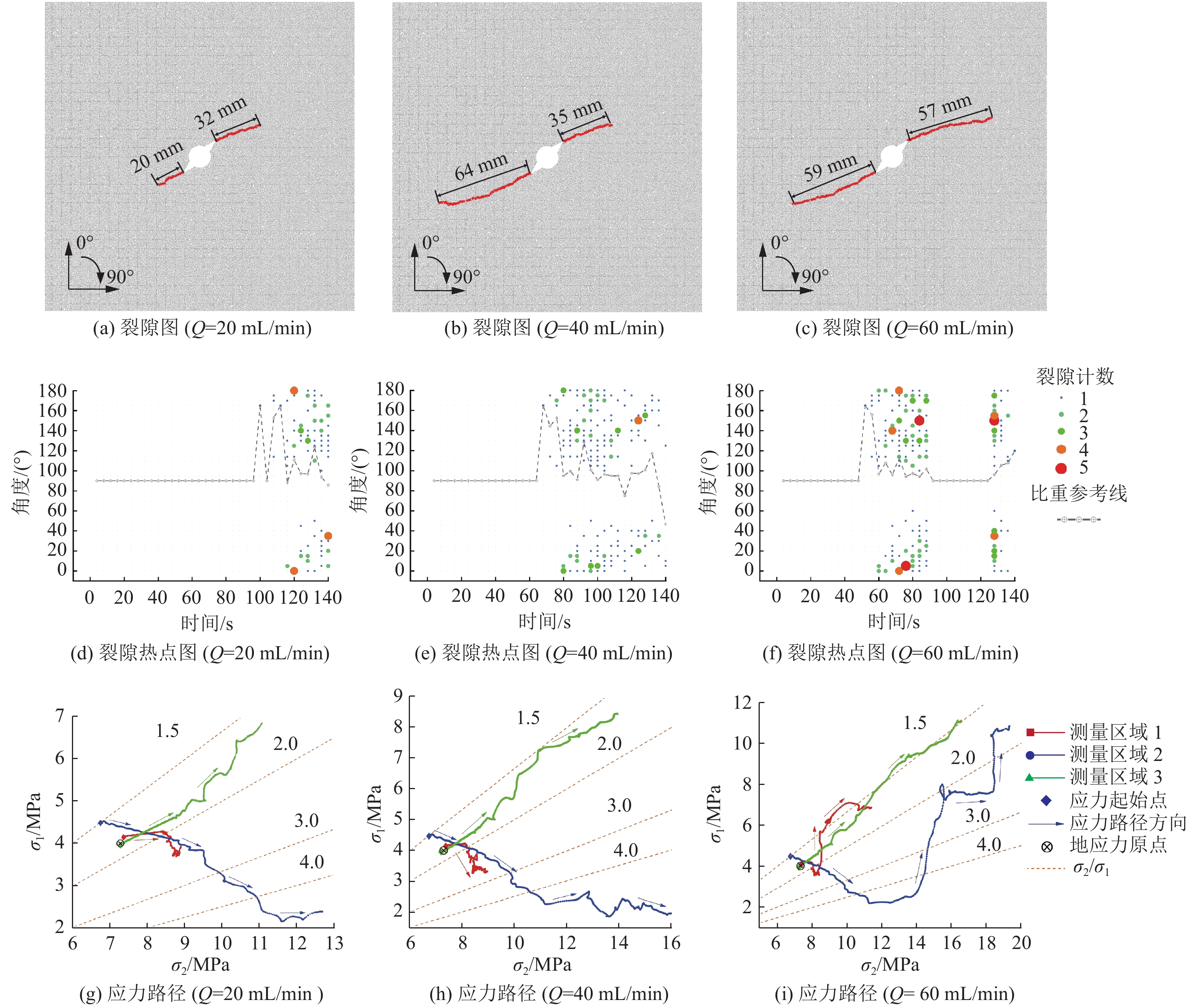
在裂隙表征方面,由于离散元模型精度的原因及颗粒的不连续性,宏观裂隙的扩展方向并不能由微裂隙的扩展方向直接表示,而是通过微裂隙在一个时间段内各个方向上的分布比重体现的,如图5、图6d所示。裂隙热点图可表明压裂过程中每隔4 s各个角度范围内的裂隙扩展数量,灰色虚线为比重参考线,代表每个时间间隔内角度的平均值,均值处于90°表明宏观裂隙沿原有方向扩展。在应力表征方面,应力路径能描述某一区域及其附近局部主应力的变化情况,通过统计不同时间点每个监测区域的最大主应力,并将其按时间顺序连接成线得到;根据最大周向拉应力准则,一定程度上可用于判断该区域在压裂过程中裂隙在每个时间点扩展方向的可能性及附近裂隙尖端的应力状态[26],黄色虚线(图6g、图6h、图6i)为恒定应力比参考线,代表σ2/σ1的比值。
3.1 不同排量下水力压裂应力与裂隙细观演化规律
图6为不同排量下水力压裂裂隙分布、裂隙热点及应力路径对比。当煤体物性参数一致时(方案设计1、2、3号实验),如图6a—图6c所示,压裂排量越大,压裂半径越大;压裂平均半径从20 mL/min条件下的26 mm增加到了60 mL/min条件下的58 mm,增加为原来的2.2倍。从图6d—图6f中可以看出,压裂排量越大,裂隙产生的时间越早,即起裂时间越短,且高排量情况下,裂隙扩展的大事件数量及有信号的时间段都有较大增加。当压裂排量为60 mL/min时,出现了裂隙的二次扩展现象,在90~130 s时出现了裂隙扩展的空白期;可能原因是较高压裂排量导致了裂隙的快速扩展,而在裂隙扩展后由于裂隙容水体积迅速增加,导致水压下降明显,不足以让裂隙尖端产生足够的应力条件使裂隙继续扩展,致使裂隙扩展暂时停滞。3种排量下,虽然起裂初期微裂隙角度均值偏离90°较大,但产生的裂隙数量较少,对裂隙原有的扩展方向影响程度不明显;起裂经过20 s后,微裂隙均值主要分布在90°~120°范围内,随着微裂隙数量的逐渐增加,宏观裂隙扩展方向由45°向90°推进,偏转程度逐渐增加。
应力演化方面,如图6g—图6i所示,由于压裂孔和导向槽的存在,3个区域内的初始地应力状态均有一定程度的偏移,其中2号区域偏移程度最大,均向着低局部应力比值的方向发展。20 mL/min和40 mL/min排量下,压裂过程中3个测量区域内的应力演化方向及最终应力路径曲线形状较为相似,而在60 mL/min排量下,上述特征会有明显的改变。在压裂排量为20 mL/min和40 mL/min时,1号区域和2号区域的局部主应力向着更高应力比的方向发展,且2号区域σ2/σ1的增加更为明显。随着1号区域和2号区域σ2/σ1的增加,裂隙扩展逐渐偏向X轴方向。而3号区域的σ2/σ1值在1.5~2.0的范围内波动,其数值与原始地应力状态比值大致相同,但数值在压裂过程中不断增大,应力集中现象较为明显。说明随着压裂的进行,裂隙尖端附近的应力比值在不断增大,使得裂隙的后续扩展受局部地应力的影响逐渐增加,从而偏离原有的扩展方向。在压裂排量为60 mL/min时,1号区域与3号区域应力演化方向类似,且σ2/σ1相较原始比值变化不大;而2号区域σ2/σ1在压裂后期向着比值较小的方向发展,说明随着压裂排量的升高,裂隙沿原有方向的扩展能力也会随之加强,抵抗一部分由于局部地应力作用而产生的裂隙偏转现象,与图6c所示结果相对应。
3.2 不同泊松比下水力压裂应力与裂隙细观演化规律
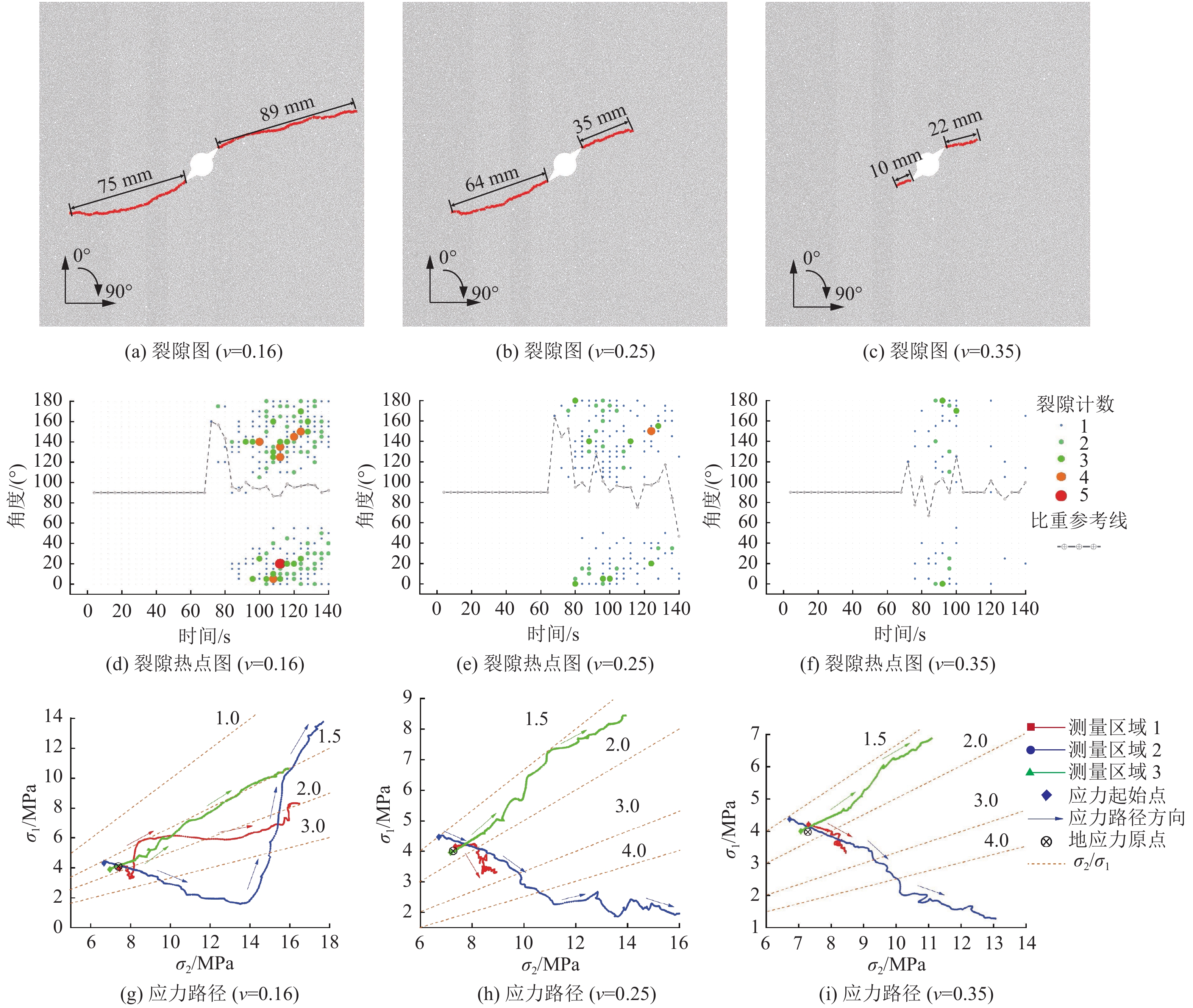
当压裂排量为40 mL/min时(方案设计2、4、5号实验),如图7a—图7c所示,随着试件泊松比的升高,压裂半径急剧降低,压裂平均半径从ν= 0.16条件下的82 mm减少到了ν= 0.35 条件下的16 mm。由图7d—图7f中可以看出,煤体泊松比的变化对试件的起裂时间影响不明显,3个试件均在压裂80 s后起裂,但泊松比会严重影响试件最终的裂隙发育情况及裂隙扩展的大事件数量,因此,具有较高泊松比的煤体更难压裂。
应力演化特征如图7g—图7i所示,ν=0.16试件的应力演化趋势表现出与压裂排量为60 mL/min的情况类似,1号和3号区域σ2/σ1保持在1.5~2.0附近波动,而2号区域σ2/σ1先升高再降低。ν= 0.35试件的应力演化趋势表现出与压裂排量为20 mL/min的情况类似,3号区域σ2/σ1保持在1.5~2.0附近波动,而1号和2号区域σ2/σ1一直处于上升趋势。在不含天然裂隙试件的应力演化过程中,除去水压对地应力的扰动作用,只有裂隙扩展对局部地应力的分布会有影响,此处未考虑压裂过程中瓦斯流动及煤体遇水软化造成的孔隙压力变化。结合裂隙分布图可以得出,水力压裂过程中,压裂孔附近的应力演化方向及最终应力路径曲线形状受当前裂隙扩展情况影响显著,而这种裂隙扩展情况无论是压裂排量还是泊松比所导致,并不会影响其与应力路径的对应关系。
3.3 不同天然裂隙密度下水力压裂应力与裂隙细观演化规律
当压裂排量和煤体力学参数一定时(方案设计6、7、8号实验),如图8a—图8c所示,天然裂隙密度越高,水力裂隙的形状越复杂,且裂隙扩展的方向性几乎没有规律可循。可能原因是在较高的天然裂隙密度条件下,如碎裂煤或碎粒煤,供压裂液滤失的通道显著增加,导致新裂隙产生较少,压裂液更多的是对原有天然裂隙的扩展。从图8d—图8f中可以看出,在相同的压裂条件下,随着天然裂隙密度的升高,起裂时间并没有发生较为明显的改变,均在压裂60 s后开始起裂;但在60~140 s裂隙扩展阶段,微裂隙在各个角度上的数量都有显著的降低趋势;且微裂隙角度均值波动程度逐渐增大,没有明显的偏向性。因此,天然裂隙发育程度高的煤体,其水力裂隙走向受天然裂隙影响明显,且多条水力裂隙被天然裂隙捕获,扩展方向受限。
应力演化特征如图8g—图8i所示,随着天然裂隙密度的增加,3个区域应力演化的规律性逐渐减弱,且应力变化幅度逐渐减小;初始地应力状态的偏移程度相较于完整试件更加明显,偏离值上升了一个数量级,偏离范围由0.1~1.0 MPa增至1.0~5.0 MPa,偏离位置也由于天然裂隙的随机性而无法预测。
天然裂隙密度较低时,如裂隙发育程度较低的原生结构煤,应力演化方向及最终应力路径曲线形状与压裂排量为60 mL/min的情况类似,3号区域均在压裂后期由局部高地应力比值向低应力比值方向发展。天然裂隙密度中等时,上述应力特征与压裂排量为20 mL/min和40 mL/min的情况类似,1号区域应力状态整体变化不大,σ2/σ1在1.5~2.0之间波动;3号区域σ2/σ1不变但σ1随σ2的增大而增大;2号区域σ2/σ1在不断增大,由1.6增加到10.0以上,该区域裂隙沿X轴扩展的概率随压裂过程逐渐增大。当天然裂隙密度较高时,如碎裂煤,由于天然裂隙的影响,3个区域内的应力演化特征没有较好的规律性,多个区域出现了应力演化方向的反转现象,应力状态更加随机,难以预测。
因此,高裂隙发育的煤层地应力状态更加复杂,煤层整体地应力状态并不能代表局部应力状态,对于该类煤层的增透方案设计需要因地制宜。
3.4 工程应用模式探讨
研究结果表明,压裂排量的增加导致压裂半径也随之增加,但泊松比较高的煤层水力裂隙很难扩展,这一结论与董卓等[11]的研究结果得到很好地相互印证。因此,针对泊松比较高的煤层,压裂方案设计需要考虑更多的因素;而天然裂隙发育过高的煤层,裂隙的扩展方向几乎无法预测,并且由于压裂液滤失严重,存在无法蹩压的现象,需要更大的压裂排量达到相同的压裂效果。
另一方面,低压裂排量、中天然裂隙密度和高泊松比试件的应力演化方向及最终应力路径曲线形状类似,而高压裂排量、低泊松比和低天然裂隙密度试件的上述应力特征类似,对比其宏观裂隙分布图,可以得出某一区域应力路径的演化特征能够反映出裂隙的扩展状态,并且这种应力演化特征与裂隙扩展状态的对应关系只与当前地应力情况及裂隙扩展情况有关,而与何种因素导致的这种裂隙扩展状态关系不大。因此,该方法为压裂范围的监测提供了一条新的思路:在压裂前期,现场可设置几组应力监测区域记录并评估压裂区的应力路径曲线和缝网扩展情况,在后续压裂施工过程中可将此次应力路径曲线与先前的压裂数据进行对比分析,结合其他压裂范围监测手段如微震、瞬变电磁等,可更加精确地判断该次压裂缝网的扩展范围。但天然裂隙发育的煤层由于应力分布的复杂性,该方法并不适用。
4 结 论
a. 随着压裂排量的增加,压裂半径逐渐增大,并且出现了裂隙的二次扩展现象;不同压裂排量下的应力演化方向及最终应力路径曲线形状有着明显的不同,低排量条件下裂隙附近的应力比值逐渐增大,而在高排量条件下先增大后减小。
b. 煤层泊松比越大,平均压裂半径越低,但对起裂时间及裂隙的扩展形态影响不明显;低泊松比与高压裂排量试件的应力演化方向及最终应力路径曲线形状较为类似,高泊松比与低压裂排量试件的上述特征较为类似。
c. 煤体天然裂隙的发育情况对水力裂隙的扩展起着关键性作用,天然裂隙密度越高,裂隙形态越复杂,扩展越没有方向性,且新产生的裂隙很少;含天然裂隙煤体初始应力状态相较于原生结构煤偏移更加明显,应力演化方向在高天然裂隙发育情况下还会出现反转现象。
d. 通过不同因素下水力压裂裂隙扩展形态及应力路径特征的对比分析,得出应力演化方向及最终应力路径曲线形状受当前裂隙扩展状态的影响显著,现场可通过在压裂区域进行应力监测,结合微震等其他压裂监测手段,更为精确地判断压裂缝网的扩展范围。
-
表 1 试样宏观参数与模型宏观参数的比较
Table 1 Comparison between sample macro parameters and model macro parameters
宏观力学参数 实际值 PFC2D
计算值误差/% 单轴抗压强度σc/MPa 32.22 32.04 −0.5 弹性模量E/GPa 1.81 1.82 0.5 泊松比ν 0.25 本体抗拉强度σt/MPa 2.83 2.96 4.6 表 2 模型细观参数
Table 2 Model mesoscopic parameters
参数类别 细观参数 数值 颗粒 颗粒最小半径Rmin/mm 0.30 最大最小粒径比Rmax/Rmin 1.66 颗粒密度ρ/(kg∙m−3) 1 280 孔隙率/% 9 阻尼β/(Ns∙m−1) 0.50 接触模型 细观弹性模量Ec/GPa 1.00 刚度比kn/ks 2.30 摩擦因数μ 0.50 细观抗拉强度σc/MPa 11 黏聚力c/MPa 20 摩擦角φ/(°) 37.50 法向临界阻尼比βn 0.57 表 3 水力压裂模拟方案设计
Table 3 Scheme design of hydraulic fracturing simulation
序号 天然裂隙
密度煤体泊松比 压裂排量Q/(mL∙min−1) 1 无 0.25 20 2 无 0.25 40 3 无 0.25 60 4 无 0.16 40 5 无 0.35 40 6 低 0.25 40 7 中 0.25 40 8 高 0.25 40 注:低、中、高泊松比分别代表ν = 0.16、ν = 0.25、ν = 0.35;低、中、高压裂排量分别代表Q = 20、Q = 40、Q = 60 mL/min;低、中、高天然裂隙密度分别代表与参考线相交的裂隙数量为5、10、20个。 -
[1] ZHANG Chaolin,WANG Enyuan,XU Jiang,et al. A new method for coal and gas outburst prediction and prevention based on the fragmentation of ejected coal[J]. Fuel,2021,287:119493. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119493
[2] 陈月霞,褚廷湘,陈鹏,等. 瓦斯抽采钻孔间距优化三维数值模拟量化研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2021,49(3):78−84. CHEN Yuexia,CHU Tingxiang,CHEN Peng,et al. Quantitative study of 3D numerical simulation on optimizing borehole layout spacing of gas drainage[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2021,49(3):78−84. CHEN Yuexia, CHU Tingxiang, CHEN Peng, et al. Quantitative study of 3D numerical simulation on optimizing borehole layout spacing of gas drainage[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(3): 78–84.
[3] TAO Shu,PAN Zhejun,TANG Shuling,et al. Current status and geological conditions for the applicability of CBM drilling technologies in China:A review[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2019,202:95−108. DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2018.11.020
[4] 李全贵,翟成,林柏泉,等. 定向水力压裂技术研究与应用[J]. 西安科技大学学报,2011,31(6):735−739. LI Quangui,ZHAI Cheng,LIN Baiquan,et al. Research and application of directional hydraulic fracturing technology[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology,2011,31(6):735−739. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9315.2011.06.021 LI Quangui, ZHAI Cheng, LIN Baiquan, et al. Research and application of directional hydraulic fracturing technology[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2011, 31(6): 735–739. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9315.2011.06.021
[5] ZHENG Chunshan,JIANG Bingyou,XUE Sheng,et al. Coalbed methane emissions and drainage methods in underground mining for mining safety and environmental benefits:A review[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection,2019,127:103−124. DOI: 10.1016/j.psep.2019.05.010
[6] 程玉刚. 煤层水压裂缝导向扩展控制机理及方法[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2018. CHENG Yugang. The mechanism and method of directional hydraulic fracturing in coal seam[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2018.
[7] 白雪元, 王学滨, 刘桐幸. 考虑单元劈裂的流–固耦合连续–非连续方法及定向水力压裂模拟[J/OL]. 计算力学学报, 2021: 1−8[2022-04-08]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1373.O3.20210927.2059.005.html. BAI Xueyuan, WANG Xuebin, LIU Tongxing. A fluid−solid coupling continuum−discontinuum method considering element splitting and simulation of directional hydraulic fracturing[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2021: 1–8 [2022-04-08]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1373.O3.20210927.2059.005.html.
[8] 董卓,唐世斌. 基于最大周向应变断裂准则定向射孔水力裂缝扩展研究[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(11):4543−4553. DONG Zhuo,TANG Shibin. Oriented perforation hydraulic fracture propagation based on the maximum tangential strain criterion[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2019,40(11):4543−4553. DONG Zhuo, TANG Shibin. Oriented perforation hydraulic fracture propagation based on the maximum tangential strain criterion[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(11): 4543–4553.
[9] WANG Tao,HU Wanrui,ELSWORTH D,et al. The effect of natural fractures on hydraulic fracturing propagation in coal seams[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2017,150:180−190. DOI: 10.1016/j.petrol.2016.12.009
[10] 刘顺,何衡,赵倩云,等. 水力裂缝与天然裂缝交错延伸规律[J]. 石油学报,2018,39(3):320−326. LIU Shun,HE Heng,ZHAO Qianyun,et al. Staggered extension laws of hydraulic fracture and natural fracture[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2018,39(3):320−326. DOI: 10.7623/syxb201803007 LIU Shun, HE Heng, ZHAO Qianyun, et al. Staggered extension laws of hydraulic fracture and natural fracture[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(3): 320–326. DOI: 10.7623/syxb201803007
[11] GE Zhaolong,ZHONG Jianyu,LU Yiyu,et al. Directional distance prediction model of slotting–directional hydraulic fracturing (SDHF) for coalbed methane (CBM) extraction[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2019,183:106429. DOI: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106429
[12] CHENG Yugang,LU Yiyu,GE Zhaolong,et al. Experimental study on crack propagation control and mechanism analysis of directional hydraulic fracturing[J]. Fuel,2018,218:316−324. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.01.034
[13] 吴拥政,杨建威. 煤矿砂岩横向切槽真三轴定向水力压裂试验[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(3):927−935. WU Yongzheng,YANG Jianwei. True tri-axial directional hydraulic fracturing test on sandstone with transverse grooves in coal mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(3):927−935. WU Yongzheng, YANG Jianwei. True tri-axial directional hydraulic fracturing test on sandstone with transverse grooves in coal mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(3): 927–935.
[14] 贾奇锋,倪小明,赵永超,等. 不同煤体结构煤的水力压裂裂缝延伸规律[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2019,47(2):51−57. JIA Qifeng,NI Xiaoming,ZHAO Yongchao,et al. Fracture extension law of hydraulic fracture in coal with different structure[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2019,47(2):51−57. JIA Qifeng, NI Xiaoming, ZHAO Yongchao, et al. Fracture extension law of hydraulic fracture in coal with different structure[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2019, 47(2): 51–57.
[15] 何涛. 煤岩组合体力学模型及细观损伤过程的颗粒流分析[J]. 煤矿安全,2018,49(11):160−163. HE Tao. Mechanical model of coal and rock mass and particle flow analysis of mesoscopic damage process[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2018,49(11):160−163. HE Tao. Mechanical model of coal and rock mass and particle flow analysis of mesoscopic damage process[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2018, 49(11): 160–163.
[16] 王云飞,黄正均,崔芳. 煤岩破坏过程的细观力学损伤演化机制[J]. 煤炭学报,2014,39(12):2390−2396. WANG Yunfei,HUANG Zhengjun,CUI Fang. Damage evolution mechanism in the failure process of coal rock based on mesomechanics[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2014,39(12):2390−2396. WANG Yunfei, HUANG Zhengjun, CUI Fang. Damage evolution mechanism in the failure process of coal rock based on mesomechanics[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(12): 2390–2396.
[17] 刘斌,赵毅鑫,张汉,等. 单轴压缩及劈裂试验下煤的声发射特征研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2020,37(3):613−621. LIU Bin,ZHAO Yixin,ZHANG Han,et al. Acoustic emission characteristics of coal under uniaxial compression and Brazilian splitting[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2020,37(3):613−621. LIU Bin, ZHAO Yixin, ZHANG Han, et al. Acoustic emission characteristics of coal under uniaxial compression and Brazilian splitting[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2020, 37(3): 613–621.
[18] 陈鹏宇. PFC2D模拟裂隙岩石裂纹扩展特征的研究现状[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(2):528−539. CHEN Pengyu. Research progress on PFC2D simulation of crack propagation characteristics of cracked rock[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(2):528−539. CHEN Pengyu. Research progress on PFC2D simulation of crack propagation characteristics of cracked rock[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(2): 528–539.
[19] POTYONDY D O,CUNDALL P A. A bonded–particle model for rock[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2004,41(8):1329−1364. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.09.011
[20] WANG Tao,ZHOU Weibo,CHEN Jinhua,et al. Simulation of hydraulic fracturing using particle flow method and application in a coal mine[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology,2014,121:1−13. DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2013.10.012
[21] CHONG Zhaohui,LI Xuehua,CHEN Xiangyu. Effect of injection site on fault activation and seismicity during hydraulic fracturing[J]. Energies,2017,10:1619. DOI: 10.3390/en10101619
[22] 张玉旗. 定向水力压裂裂纹扩展规律的模拟研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2019. ZHANG Yuqi. Simulation of crack propagation in directional hydraulic fracture[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2019.
[23] 夏磊,曾亚武. 基于PFC2D数值模拟的交替压裂中应力阴影效应研究[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(11):4269−4277. XIA Lei,ZENG Yawu. Stress shadow effect of alternative fracturing based on numerical simulation of PFC2D[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2018,39(11):4269−4277. XIA Lei, ZENG Yawu. Stress shadow effect of alternative fracturing based on numerical simulation of PFC2D[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(11): 4269–4277.
[24] 康红普,冯彦军. 定向水力压裂工作面煤体应力监测及其演化规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2012,37(12):1953−1959. KANG Hongpu,FENG Yanjun. Monitoring of stress change in coal seam caused by directional hydraulic fracturing in working face with strong roof and its evolution[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2012,37(12):1953−1959. KANG Hongpu, FENG Yanjun. Monitoring of stress change in coal seam caused by directional hydraulic fracturing in working face with strong roof and its evolution[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2012, 37(12): 1953–1959.
[25] CAI Jianchao,WOOD D A,HAJIBEYGI H,et al. Multiscale and multiphysics influences on fluids in unconventional reservoirs:Modeling and simulation[J]. Advances in Geo−Energy Research,2022,6(2):91−94.
[26] 张培龙. 红庆河煤矿深部开采矿压与支护技术的分析[J]. 内蒙古煤炭经济,2018,30(13):36−37. ZHANG Peilong. Analysis of deep mining pressure and support technology in Hongqinghe coal mine[J]. Inner Mongolia Coal Economy,2018,30(13):36−37. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0155.2018.13.020 ZHANG Peilong. Analysis of deep mining pressure and support technology in Hongqinghe coal mine[J]. Inner Mongolia Coal Economy, 2018, 30(13): 36–37. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0155.2018.13.020
-
期刊类型引用(15)
1. 孟永兵,黄庆享,贺雁鹏,范东林,陈苏社,韦业豪,王君. 浅埋近距离煤层工作面过平行煤柱开采强矿压显现规律. 西安科技大学学报. 2024(02): 245-255 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陆泳鑫,胡胜勇,李国富,武玺,路佳旗,杨育涛,张村,苏燕. 采空区下伏煤层水力压裂试验研究与应用. 煤炭科学技术. 2024(04): 231-242 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 邹军. 低透气性突出煤层群首采层水力割缝卸压抽采技术研究. 中国煤炭. 2024(06): 52-58 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 乔伟. 基于多孔水力压裂的硬岩快速掘进技术研究. 山东煤炭科技. 2024(06): 38-42 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 郑春山,韩飞林,江丙友,薛生,李国富,刘帅丽. 煤体原位水力压注多尺度孔裂隙演化及渗透率跃变规律. 中国矿业大学学报. 2024(04): 710-725 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 侯公羽,刘云峰,于续楠,周光一,邵耀华,尚宇豪. 基于不同断裂准则下水力压裂裂纹起裂规律研究. 矿业科学学报. 2024(05): 687-697 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 张跃兵,胡千庭,李全贵,宋明洋,武文宾,曹偈. 软煤水力压裂孔周应力的时空演化研究. 矿业安全与环保. 2024(05): 1-7+14 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 冯欣雨,肖晖,李泉辉,梁朝阳,钟国海,刘峻溢,秦启雯. 致密砂岩水力裂缝特征实验研究. 非常规油气. 2023(04): 132-138 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 张洁,曹函,杜宗霖,杨四方. 基于天然裂缝网络的页岩力学性质数值模拟研究. 科技通报. 2023(11): 57-67 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 王超,杨盼盼,南童昕,郭玉龙. 基于XFEM的煤矿巷道顶板裂隙扩展特征研究. 煤炭技术. 2023(12): 32-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 陈冬冬,王建利,贾秉义,席杰. 碎软煤层顶板梳状长钻孔水力压裂区域瓦斯高效抽采模式. 煤田地质与勘探. 2022(08): 29-36 .  本站查看
本站查看
12. 翟成,郑仰峰,余旭,徐吉钊,孙勇,丛钰洲,唐伟,李宇杰,朱薪宇,陈爱坤. 水力压裂模拟用煤岩体相似材料基础力学特性实验研究. 煤田地质与勘探. 2022(08): 16-28 .  本站查看
本站查看
13. 李全贵,武晓斌,胡千庭,刘乐,石佳林,宋明洋. 含结构面相似材料水力裂缝演化的实验研究. 煤田地质与勘探. 2022(08): 45-53 .  本站查看
本站查看
14. 王世斌,王刚,陈雪畅,范酒源,迟利辉. 基于PFC~(2D)-COMSOL的煤层水力压裂增透促抽瓦斯数值模拟研究. 煤矿安全. 2022(10): 132-140 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 李全贵,邓羿泽,胡千庭,武晓斌,王晓光,姜志忠,刘乐,钱亚楠,宋明洋. 煤岩水力压裂物理试验研究综述及展望. 煤炭科学技术. 2022(12): 62-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(16)







 下载:
下载: